Product Description
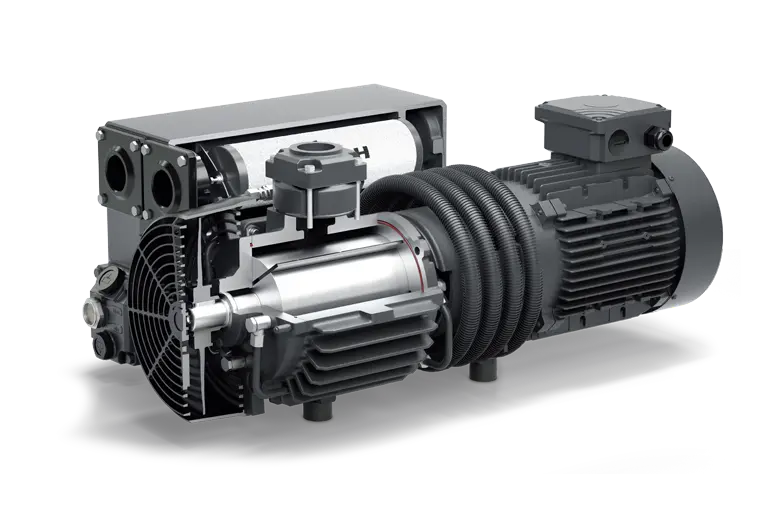
CHINAMFG Tunland Pickup auto parts vacuum pump for CHINAMFG ISF2.8 diesel engine
| Product name | vacuum pump for CHINAMFG ISF2.8 |
| Model | |
| OEM | 5282085 |
| Application | Cummins ISF2.8 diesel engine |
| MOQ | 2 pcs |
| Package | carton box or wooden box, packed by pallet |
| Leading time | depends on stock quantity and order quantity |
| Shipping terms | EXW, FOB, CIF, etc. |
| Port | HangZhou port, ZheJiang port |
| Payment | T/T (wire transfer), western union, L/C, etc. |
| Warranty | 12 month |
What products we can supply to customers :
1) Cylinder head, cylinder head assembly, cylinder block, crankshaft for : Toyota, VW, Mitsubishi, Hyundai, KIA, ISUZU, Ford, Nissan, Mazda, Cummins, Great Wall, CAT, HINO, Komatsu, Kubota, etc.
2) Engine long block / bare engine, engine short block for : Toyota, CHINAMFG / KIA, Cummins, Great Wall, Haval, Mitsubishi, etc.
3) Full series of engine spare parts for some models: such as 4Y, ISF2.8, ISF3.8, GW4D20, GW4G15, GW2.8, etc.
Related engine parts we can supply:
Cylinder head series:
Cylinder head for the following car engines:
Cylinder head for VW/Audi/Skoda: CAYA, CAYB, CAYC, CAYD, CAYE, ADR, AMK, AMU, ANB, AAB, BLR, BLX, BLY, BVX, BVY, AXX, BPG, BWA, CAAA, CAAB, CAAC, CCHB, CDBA, CDCA, CKTB, CFCA, AZV, BKD, AXD, AXE, BAC, etc.
Cylinder head for Toyota: 1KD-FTV, 2KD-FTV, 3C-TE, 2C-TE, 1C, 1NZ/2NZ, 1AZ, 2AZ, 1KZ-T, 1KZ-TE, 1ZZ, 2ZZ, 2E, 3Y, 4Y, 2L, 2LT, 3L, 5L, 1DZ, 2L2, 1Z/2Z, 1HZ, 1HD, 14B, 22R,2TR, 1KD, 2KD, 1RZ/2RZ, etc.
Cylinder head for CHINAMFG & KIA: G4EK, G4EE, G4ED, G4EC, G4GC, G4HG, G4EA, D4EA, D4FA, D4EB, D4CB, 4D56, D4BH, D4BA, 4D56T, D4BF, JT, F8, J2, etc.
Cylinder head for ISUZU: 4JG2, 4HK1, 4HE1, 4HF1, 4HG1, 6HK1, 4BA1, 4BD1, 4BD2, 4BE1, 3LD1, 6SD1, C240, G16B, 4JJ1, 4JX1, 4ZD1, 4ZE1, etc.
Cylinder head for Mitsubishi: 4D30/4D36, 4M40, 4M40T, 4M41, 6D14, 6D15, 6D16, 6D17, 4DR5, 4DR7, S4S, 4D56, 4D56U, D4BH, D4BA, 4D56T, 4D55T, D4BF, 4M42, 4G64, 4G63, etc.
Cylinder head for Mazda: WL, WLT, R2, RF, WE, WLAT, NA, F8, FE
Cylinder head for Nissan: TD23, TD25, TD27, TD42, QD32, SD25, BD25, BD30, KA24, YD25, Z24, ZD30, H20-2, YD22, QR20, QR25, K21, K25, ZD3200, ZD3202, etc.
Cylinder head for Ford: WL, WL-T, WE, WLAT, R2, RF, Transit 2.4, 4D56, DV, HHDB, D4BH, P8FA, QVFA, 4D55, P4AT, DDR5, CYRA, etc.
Cylinder head for HINO: J08C/J08E, J05E, J05C, N04C, W04C/W04D, E13C, P11C, EB300, EH700, etc.
Cylinder head for DEUTZ: 30D, 52D, 56D, 65D, 1015, 226B, etc.
Cylinder head for Kubota: V1505, V2203/V2403, V1702/V1902, V3300, D1005/D1105/D1100/D1102, D722/D782/D850/D902/D905, D1302/D1402/D1403, Z750, D1703/D1503
Cylinder head for Komatsu: S6K, 4D95, 4D95S/L, 6D95, 6D125, etc.
Cylinder head for CAT: C12,C13, C15, 1N4304, etc.
Cylinder head for Cummins: ISF2.8, ISF3.8, 4BT, 6BT, 6CT, K19, etc.
Cylinder block, short block, engine long block/bare engine for the following models:
For CHINAMFG Cummins: ISF2.8, ISF3.8, 4BT, 6BT, etc.
For Great Wall: GW4D20, GW4D20B, GW4G15, GW4G15B/T, GW2.8TC, GW2.8TDI, GWTDI-2, GW2.8TC-2, CA4D28C4-1A, etc.
For CHINAMFG series: 4Y, 3Y, 1AZ, 2AZ, 3GR, 5GR, 2TR, 1ZR, 2ZR, 2L, 3L, 5L, etc.
For Hyundai/KIA series: G4FA, G4FC, G4FD, G4FG, G4FJ, G4LC, G4NA, G4NB, G4KA, G4KC, G4KD, G4KE, G4KJ, G4KH, D4CB,
For CHINAMFG series: 4A91, 4A92, 4A91T, 4G43T, 4G64, 4G69, etc.
For JAC car series: 4GB1, 4GB2, 4GB3, 4GA1, 4GA3, 4DA1, etc.
For VW car series: EA111, EA888, etc.
For CHINAMFG series: 4JB1, 4HF1, 4HG1, 4HK1, 4HE1, 4JJ1, etc.
Our advantage:
1) Engine long block are assembed by brand new original engine spare parts.
2) Long warranty period for products, warranty for 12 month.
3) Rich experience on engine parts industry, has a wide and complete supply chain.
Package and delivery:
Package by wooden box or carton box according to different models, delivery can be made by seaway, railway by FOB, CFR, CIF terms, etc.
FAQ:
Q: What is your business scope?
A: We have a wide business scope, include bare cylinder head (some models has complete cylinder head), bare cylinder block, engine long block, crankshaft, engine short block, etc. Our engine long block is assembled by original brand new spare parts, with a high quality and long warranty period. We also can supply complete engine for such models, and also can supply full series of engine spare parts for some models.
Q: What is your payment terms?
A: Payment can be made by T/T(wire transfer), L/C, Western Union, etc. Depends on different order amount, usually 30% to 50% deposit before production, balance to be payed before shipment. Payment terms is negotiable.
Q: What is the package?
A: According to different model’s weight, goods will be packed by wooden box or cartoon box, all goods will be packed by pallet before shipment.
Q: What is warranty period?
A: Warranty period for 12 month after goods sold out.
Q: What is the leading time?
A: Leading time need to be confirmed by exact model and quantity.
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| Certification: | CCC, ISO9001 |
|---|---|
| Standard Component: | Standard Component |
| Technics: | Casting |
| Material: | Vacuum Pump |
| Type: | Vacuum Pump |
| Transport Package: | Carton Box |
| Customization: |
Available
|
|
|---|

What Is the Impact of Altitude on Vacuum Pump Performance?
The performance of vacuum pumps can be influenced by the altitude at which they are operated. Here’s a detailed explanation:
Altitude refers to the elevation or height above sea level. As the altitude increases, the atmospheric pressure decreases. This decrease in atmospheric pressure can have several effects on the performance of vacuum pumps:
1. Reduced Suction Capacity: Vacuum pumps rely on the pressure differential between the suction side and the discharge side to create a vacuum. At higher altitudes, where the atmospheric pressure is lower, the pressure differential available for the pump to work against is reduced. This can result in a decrease in the suction capacity of the vacuum pump, meaning it may not be able to achieve the same level of vacuum as it would at lower altitudes.
2. Lower Ultimate Vacuum Level: The ultimate vacuum level, which represents the lowest pressure that a vacuum pump can achieve, is also affected by altitude. As the atmospheric pressure decreases with increasing altitude, the ultimate vacuum level that can be attained by a vacuum pump is limited. The pump may struggle to reach the same level of vacuum as it would at sea level or lower altitudes.
3. Pumping Speed: Pumping speed is a measure of how quickly a vacuum pump can remove gases from a system. At higher altitudes, the reduced atmospheric pressure can lead to a decrease in pumping speed. This means that the vacuum pump may take longer to evacuate a chamber or system to the desired vacuum level.
4. Increased Power Consumption: To compensate for the decreased pressure differential and achieve the desired vacuum level, a vacuum pump operating at higher altitudes may require higher power consumption. The pump needs to work harder to overcome the lower atmospheric pressure and maintain the necessary suction capacity. This increased power consumption can impact energy efficiency and operating costs.
5. Efficiency and Performance Variations: Different types of vacuum pumps may exhibit varying degrees of sensitivity to altitude. Oil-sealed rotary vane pumps, for example, may experience more significant performance variations compared to dry pumps or other pump technologies. The design and operating principles of the vacuum pump can influence its ability to maintain performance at higher altitudes.
It’s important to note that vacuum pump manufacturers typically provide specifications and performance curves for their pumps based on standardized conditions, often at or near sea level. When operating a vacuum pump at higher altitudes, it is advisable to consult the manufacturer’s guidelines and consider any altitude-related limitations or adjustments that may be necessary.
In summary, the altitude at which a vacuum pump operates can have an impact on its performance. The reduced atmospheric pressure at higher altitudes can result in decreased suction capacity, lower ultimate vacuum levels, reduced pumping speed, and potentially increased power consumption. Understanding these effects is crucial for selecting and operating vacuum pumps effectively in different altitude environments.

What Is the Difference Between Dry and Wet Vacuum Pumps?
Dry and wet vacuum pumps are two distinct types of pumps that differ in their operating principles and applications. Here’s a detailed explanation of the differences between them:
Dry Vacuum Pumps:
Dry vacuum pumps operate without the use of any lubricating fluid or sealing water in the pumping chamber. They rely on non-contact mechanisms to create a vacuum. Some common types of dry vacuum pumps include:
1. Rotary Vane Pumps: Rotary vane pumps consist of a rotor with vanes that slide in and out of slots in the rotor. The rotation of the rotor creates chambers that expand and contract, allowing the gas to be pumped. The vanes and the housing are designed to create a seal, preventing gas from flowing back into the pump. Rotary vane pumps are commonly used in laboratories, medical applications, and industrial processes where a medium vacuum level is required.
2. Dry Screw Pumps: Dry screw pumps use two or more intermeshing screws to compress and transport gas. As the screws rotate, the gas is trapped between the threads and transported from the suction side to the discharge side. Dry screw pumps are known for their high pumping speeds, low noise levels, and ability to handle various gases. They are used in applications such as semiconductor manufacturing, chemical processing, and vacuum distillation.
3. Claw Pumps: Claw pumps use two rotors with claw-shaped lobes that rotate in opposite directions. The rotation creates a series of expanding and contracting chambers, enabling gas capture and pumping. Claw pumps are known for their oil-free operation, high pumping speeds, and suitability for handling dry and clean gases. They are commonly used in applications such as automotive manufacturing, food packaging, and environmental technology.
Wet Vacuum Pumps:
Wet vacuum pumps, also known as liquid ring pumps, operate by using a liquid, typically water, to create a seal and generate a vacuum. The liquid ring serves as both the sealing medium and the working fluid. Wet vacuum pumps are commonly used in applications where a higher level of vacuum is required or when handling corrosive gases. Some key features of wet vacuum pumps include:
1. Liquid Ring Pumps: Liquid ring pumps feature an impeller with blades that rotate eccentrically within a cylindrical casing. As the impeller rotates, the liquid forms a ring against the casing due to centrifugal force. The liquid ring creates a seal, and as the impeller spins, the volume of the gas chamber decreases, leading to the compression and discharge of gas. Liquid ring pumps are known for their ability to handle wet and corrosive gases, making them suitable for applications such as chemical processing, oil refining, and wastewater treatment.
2. Water Jet Pumps: Water jet pumps utilize a jet of high-velocity water to create a vacuum. The water jet entrains gases, and the mixture is then separated in a venturi section, where the water is recirculated, and the gases are discharged. Water jet pumps are commonly used in laboratories and applications where a moderate vacuum level is required.
The main differences between dry and wet vacuum pumps can be summarized as follows:
1. Operating Principle: Dry vacuum pumps operate without the need for any sealing fluid, while wet vacuum pumps utilize a liquid ring or water as a sealing and working medium.
2. Lubrication: Dry vacuum pumps do not require lubrication since there is no contact between moving parts, whereas wet vacuum pumps require the presence of a liquid for sealing and lubrication.
3. Applications: Dry vacuum pumps are suitable for applications where a medium vacuum level is required, and oil-free operation is desired. They are commonly used in laboratories, medical settings, and various industrial processes. Wet vacuum pumps, on the other hand, are used when a higher vacuum level is needed or when handling corrosive gases. They find applications in chemical processing, oil refining, and wastewater treatment, among others.
It’s important to note that the selection of a vacuum pump depends on specific requirements such as desired vacuum level, gas compatibility, operating conditions, and the nature of the application.
In summary, the primary distinction between dry and wet vacuum pumps lies in their operating principles, lubrication requirements, and applications. Dry vacuum pumps operate without any lubricating fluid, while wet vacuum pumps rely on a liquid ring or water for sealing and lubrication. The choice between dry and wet vacuum pumps depends on the specific needs of the application and the desired vacuum level.
What Industries Commonly Rely on Vacuum Pump Technology?
Vacuum pump technology finds applications in various industries where creating and controlling vacuum or low-pressure environments is crucial. Here’s a detailed explanation:
1. Manufacturing and Production: Vacuum pumps are extensively used in manufacturing and production processes across multiple industries. They are employed for tasks such as vacuum molding, vacuum packaging, vacuum degassing, vacuum drying, and vacuum distillation. Industries like automotive, aerospace, electronics, pharmaceuticals, and food processing rely on vacuum pump technology to achieve precise and controlled manufacturing conditions.
2. Chemical and Pharmaceutical: The chemical and pharmaceutical industries heavily rely on vacuum pumps for numerous applications. These include solvent recovery, vacuum filtration, vacuum drying, distillation, crystallization, and evaporation. Vacuum pumps enable these industries to carry out critical processes under reduced pressure, ensuring efficient separation, purification, and synthesis of various chemical compounds and pharmaceutical products.
3. Semiconductor and Electronics: The semiconductor and electronics industries extensively use vacuum pumps for manufacturing microchips, electronic components, and electronic devices. Vacuum pumps are crucial in processes such as physical vapor deposition (PVD), chemical vapor deposition (CVD), etching, ion implantation, and sputtering. These processes require controlled vacuum conditions to ensure precise deposition, surface modification, and contamination-free manufacturing.
4. Research and Development: Vacuum pump technology is integral to research and development activities across scientific disciplines. It supports experiments and investigations in fields such as physics, chemistry, materials science, biology, and environmental science. Vacuum pumps facilitate processes like freeze drying, vacuum distillation, vacuum evaporation, vacuum spectroscopy, and creating controlled atmospheric conditions for studying various phenomena.
5. Food and Beverage: The food and beverage industry relies on vacuum pumps for packaging and preservation purposes. Vacuum sealing is used to extend the shelf life of food products by removing air and creating a vacuum-sealed environment that inhibits spoilage and maintains freshness. Vacuum pumps are also used in processes like freeze drying, vacuum concentration, and vacuum cooling.
6. Oil and Gas: In the oil and gas industry, vacuum pumps play a role in various applications. They are used for crude oil vacuum distillation, vacuum drying, vapor recovery, gas compression, and gas stripping processes. Vacuum pumps help maintain optimal conditions during oil refining, gas processing, and petrochemical manufacturing.
7. Environmental and Waste Management: Vacuum pumps are employed in environmental and waste management applications. They are used for tasks such as soil vapor extraction, groundwater remediation, landfill gas recovery, and wastewater treatment. Vacuum pumps facilitate the removal and containment of gases, vapors, and pollutants, contributing to environmental protection and sustainable waste management.
8. Medical and Healthcare: The medical and healthcare sectors utilize vacuum pumps for various purposes. They are used in medical equipment such as vacuum-assisted wound therapy devices, vacuum-based laboratory analyzers, and vacuum suction systems in hospitals and clinics. Vacuum pumps are also used in medical research, pharmaceutical production, and medical device manufacturing.
9. Power Generation: Vacuum pumps play a role in power generation industries, including nuclear power plants and thermal power plants. They are used for steam condensation, turbine blade cooling, vacuum drying during transformer manufacturing, and vacuum systems for testing and maintenance of power plant equipment.
10. HVAC and Refrigeration: The HVAC (Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning) and refrigeration industries rely on vacuum pumps for system installation, maintenance, and repair. Vacuum pumps are used to evacuate air and moisture from refrigerant lines and HVAC systems, ensuring optimal system performance and efficiency.
These are just a few examples of industries that commonly rely on vacuum pump technology. The versatility and wide-ranging applications of vacuum pumps make them indispensable tools across numerous sectors, enabling precise control over vacuum conditions, efficient manufacturing processes, and scientific investigations.


editor by CX 2024-03-27
